Marvelous Info About Should I Use AF-c Or AF-S
Afib With Rvr Treatment
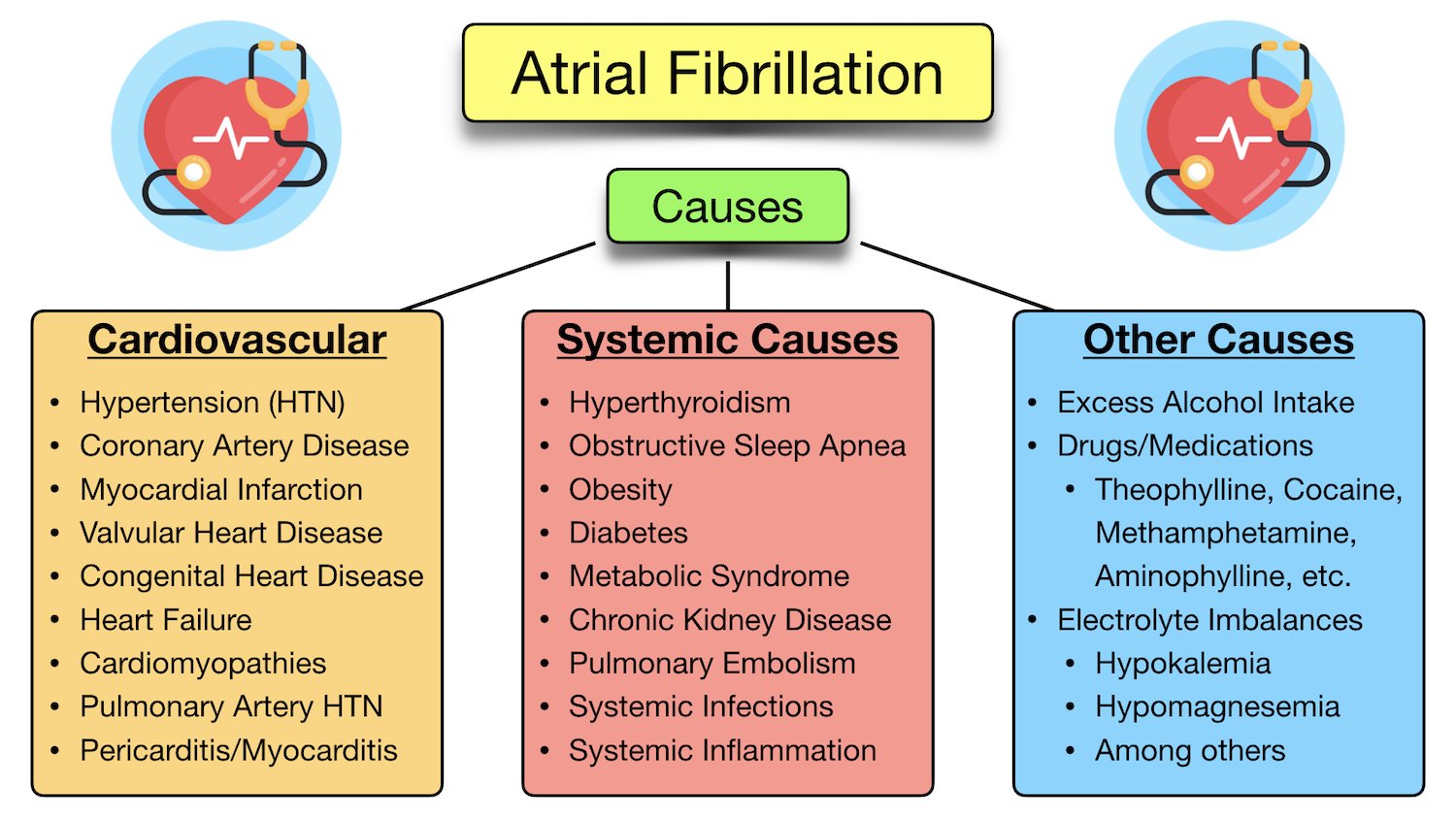
AF-C vs. AF-S
1. Understanding the Basics of Autofocus
Ever felt that sting of disappointment when you thought you nailed the perfect shot, only to find it's blurry? Yeah, we've all been there. One of the biggest culprits behind soft images is often your autofocus mode. Let's dive into two common modes: AF-C and AF-S. Knowing when to use each can be a game-changer for your photography, turning those "almost" shots into keepers. Consider this your friendly guide to navigating the autofocus maze, without all the technical jargon that makes your eyes glaze over.
Think of autofocus modes like different driving gears. You wouldn't use first gear on the highway, right? Similarly, you wouldn't use the same autofocus setting for a stationary landscape and a sprinting athlete. This article will help you select the right "gear" for every situation, leading to crisper, clearer, and more captivating images.
Before we get deeper, it is important to have the right camera setup. Check your user manual about the autofocus point placement as well. Some cameras have sophisticated subject tracking that you can turn on to help with fast moving subjects. Good light condition also help the camera acquire focus faster.
By the end of this read, you'll have a better grasp of when to deploy each autofocus mode, what makes them suitable for different scenarios, and ultimately, how to elevate the impact of your photography. So, buckle up, and let's demystify AF-C and AF-S!

The 2020 Canadian Cardiovascular Society/Canadian Heart Rhythm Society
AF-S
2. When Stability is Key
AF-S, or Single Autofocus, is your go-to option for subjects that are perfectly still. Imagine photographing a majestic mountain range, a delicate flower, or a patiently posing portrait subject. In these scenarios, the subject isn't moving, so you need an autofocus mode that locks onto the focus point and stays there. AF-S does exactly that.
Here's how it works: you half-press the shutter button, the camera focuses on your selected point, and then... it locks. It won't refocus unless you release the shutter button and press it again. This makes it ideal for situations where you have time to compose your shot carefully and ensure your subject remains stationary. Think of it as telling your camera, "Okay, focus here, and don't you dare change it!"
A common mistake is using AF-S on subjects that have small movements. A model that sway slightly or a plant that moving with the wind. It will result in blurry images because the point of focus is not where you want it to be when you finally press the shutter button. It is best to observe your subject and determine the best autofocus mode to use.
AF-S is excellent for landscapes, portraits (when the subject is relatively still), architectural shots, and product photography. Basically, anything that doesn't involve significant movement. It's reliable, accurate, and a fundamental mode for any photographer's toolkit. Once youve achieved focus using AF-S, you can often recompose your shot while holding the shutter button halfway down, ensuring the subject remains sharp. Just be mindful that significant movement after focusing will throw off the focus!

Marmoleum Installation Manual
AF-C
3. Tracking the Action
Now, let's talk about AF-C, or Continuous Autofocus (sometimes called AI Servo on Canon cameras). This mode is your secret weapon for capturing sharp images of subjects in motion. Think of a bird in flight, a child running, or a car speeding down the road. These situations demand an autofocus mode that can constantly adjust to the subject's changing position. That's where AF-C shines.
Unlike AF-S, which locks focus, AF-C continuously monitors and adjusts the focus as long as you keep the shutter button half-pressed. This means your camera is actively tracking the subject, ensuring it remains sharp even as it moves towards or away from you. It's like having a tiny, tireless assistant constantly fine-tuning the focus for you.
This makes AF-C perfect for sports photography, wildlife photography, and capturing candid moments with active children. It's also a lifesaver for events where subjects are constantly on the move, such as weddings or street performances. However, with such a powerful focusing mode, it drains the battery very quickly and it also create a lot of sound from your lens focusing and refocusing.
Using AF-C effectively requires a bit of practice. You need to learn to anticipate the subject's movement and keep your focus point trained on it. Some cameras offer advanced tracking features within AF-C, allowing you to prioritize certain subjects or adjust the sensitivity of the tracking. Experiment with these settings to find what works best for your shooting style and the types of subjects you typically photograph. Master AF-C, and you'll never miss a sharp shot of a moving subject again. It may not work on every single picture you take, so it is best to keep shooting to get that one perfect shot.
Ventricular Fibrillation Treatment
Putting it All Together
4. Situational Awareness is Key
So, you know what each mode does, but how do you decide which one to use in a real-world scenario? The key is situational awareness. Before you even raise your camera to your eye, take a moment to assess the scene. Is your subject stationary or moving? If it's moving, how fast is it moving, and is the movement predictable? Answering these questions will guide you to the right choice.
For example, if you're photographing a group of people standing still for a posed photo, AF-S is the way to go. But if those same people suddenly start running towards you in a burst of spontaneous joy (you got the perfect shot!), switch to AF-C to keep them in focus. The point is to be adaptable and responsive to the changing dynamics of the scene.
Also consider the lighting conditions. In low light, autofocus systems can struggle, regardless of the mode you're using. In these situations, you might need to switch to manual focus or use a focus assist light. And don't forget to experiment with different focus points. Single-point autofocus is great for precise control, while wide-area autofocus can be helpful for tracking erratic movement.
Ultimately, the best way to become proficient at choosing between AF-S and AF-C is to practice. Take your camera out, find different subjects, and experiment with both modes. Pay attention to the results, and learn from your mistakes. With time and experience, you'll develop an intuitive understanding of when to use each mode, allowing you to capture sharper, more compelling images in any situation. And remember, theres no shame in switching between modes mid-shoot as the situation changes!
Pin On Crk
Beyond the Basics
5. Fine-Tuning for Optimal Performance
Once you've mastered the fundamental differences between AF-S and AF-C, you can start exploring more advanced techniques to fine-tune your autofocus performance. Many cameras offer customizable settings within each mode, allowing you to tailor the autofocus behavior to specific shooting scenarios. This is where reading your camera's manual will really come in handy. Don't be afraid to dive deep into the menus and experiment with the different options.
One important setting to consider is focus priority. In AF-C mode, you can often choose between "focus priority" and "release priority." Focus priority ensures that the camera only takes a picture when the subject is in focus, while release priority allows you to take a picture even if the subject isn't perfectly sharp. For critical shots where sharpness is paramount, focus priority is the better choice. However, in fast-paced situations where you need to capture a specific moment, release priority might be preferable. You don't want to miss the peak action while your camera is hunting for focus.
Another useful technique is back-button focusing. This involves assigning the autofocus function to a separate button on the back of your camera, rather than using the shutter button. This allows you to decouple the focusing and shooting actions, giving you more control over when and how your camera focuses. It can be particularly helpful for tracking moving subjects or for quickly switching between autofocus and manual focus.
And finally, don't underestimate the power of good technique. Proper hand-holding, a stable stance, and smooth panning motions can all contribute to sharper images, regardless of the autofocus mode you're using. Practice these techniques regularly, and you'll be amazed at the improvement in your overall sharpness. Photography is more than just pointing and shooting; it's a craft that requires skill, patience, and a willingness to learn. So keep practicing, keep experimenting, and keep pushing the boundaries of your creativity. It all boils down to experience and repetition.
