Impressive Tips About Is 240V Always 3-phase
Unraveling the Mystery
1. Understanding Voltage and Electrical Systems
Let's dive straight in. When you hear "240V," does it automatically mean it's a 3-phase electrical system? The short answer is: not necessarily! While 240V can be associated with 3-phase power, it's also commonly found in single-phase setups, particularly in residential settings. Think of it like this: a sports car can go fast, but not everything that goes fast is a sports car. Voltage is simply the 'electrical pressure' that pushes current through a circuit, and 240V is just one level of that pressure.
The confusion often arises because larger appliances like electric stoves, dryers, and some air conditioning units require 240V to operate efficiently. These are generally connected to a split-phase 120/240V system, which is still considered single-phase. Imagine your home's electrical panel as a well-organized party. Some circuits are the "easy-going" 120V for lights and smaller devices. Others need a "stronger drink" (240V) to power the heavier hitters, hence the need for a more robust single-phase line.
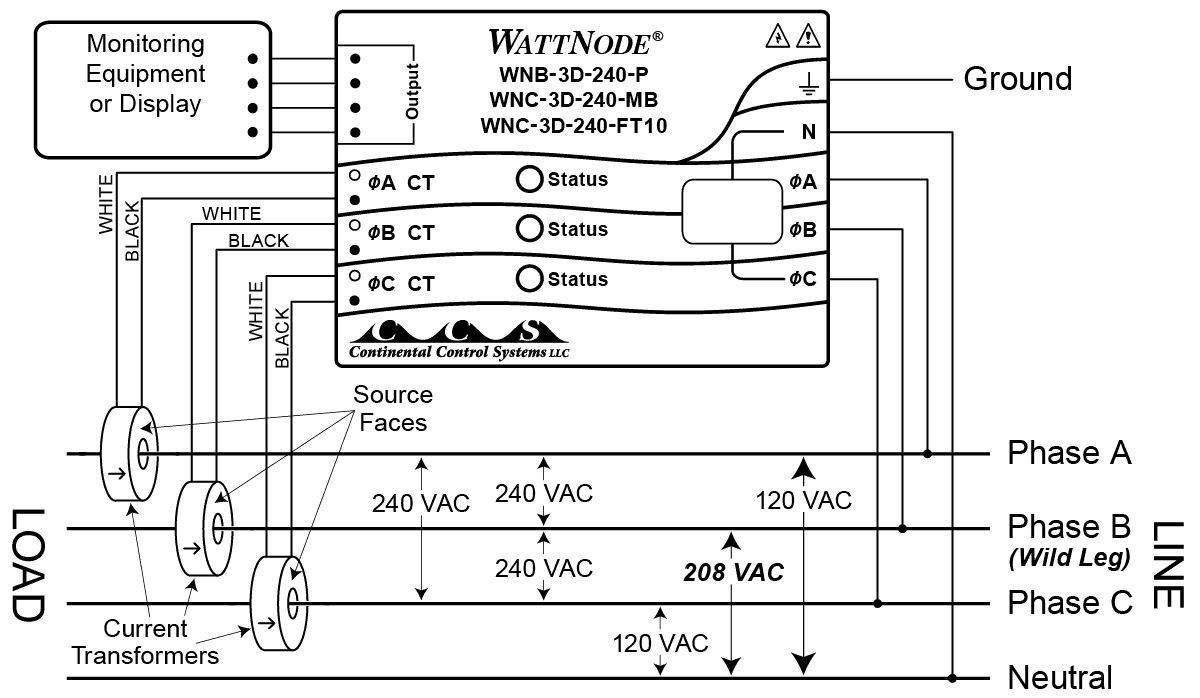
So how do you tell the difference between 240V single-phase and 240V three-phase? It comes down to the wiring and the purpose. Single-phase 240V typically involves two "hot" wires, plus a neutral and ground. Three-phase, on the other hand, has three "hot" wires, potentially a neutral, and a ground. The presence of that third 'hot' wire is the key indicator. It's like comparing a duet to a trio both can sound great, but they're built differently!
Essentially, voltage is a measure of electrical potential, and phase refers to the distribution of alternating current (AC) power. In a single-phase system, the voltage varies in a single, synchronized wave. In a three-phase system, there are three voltage waves offset from each other by 120 degrees. This staggering creates a smoother, more consistent power delivery, ideal for industrial applications. Think of it like paddling a canoe: single-phase is one person paddling, while three-phase is three people paddling in sync, resulting in a smoother ride.

Single-Phase vs. Three-Phase
2. Delving Deeper into Electrical Configurations
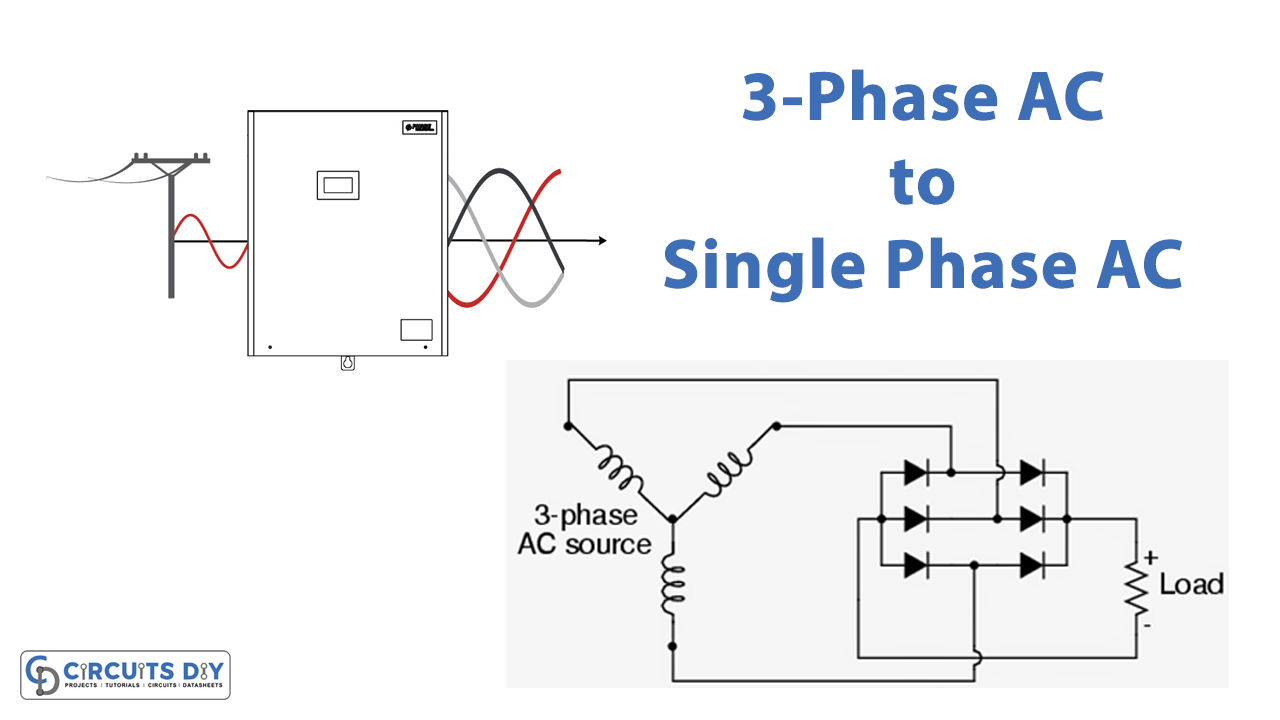
To truly understand this, we need to dissect the core differences between single-phase and three-phase power. Single-phase, as we've touched upon, is the standard in most homes. It's simpler and cheaper to implement for lower power demands. It works perfectly well for lighting, electronics, and appliances that don't require huge amounts of energy. Imagine it as your everyday car reliable, efficient, and gets the job done for most situations.
Three-phase power, however, is the workhorse of industry and large commercial buildings. It delivers power more efficiently and can handle significantly higher loads. Large motors, heavy machinery, and entire manufacturing plants rely on three-phase power for their operation. Think of it like a semi-truck designed for hauling massive loads and requiring a more complex and robust system.
Another way to visualize it is by thinking about water flowing through pipes. Single-phase is like a single pipe providing a stream of water, while three-phase is like three pipes delivering streams of water that are staggered in time, resulting in a more continuous and powerful flow. This smoother power delivery is critical for sensitive equipment and heavy-duty applications.
The choice between single-phase and three-phase ultimately depends on the power requirements of the application. For a small home with typical appliances, single-phase is more than sufficient. But for a large factory with heavy machinery, three-phase is essential. Trying to run a factory on single-phase would be like trying to pull a semi-truck with a sedan — it's simply not going to work!

Applications
3. Real-World Examples of Voltage and Phase Usage
Let's look at some practical examples to solidify your understanding. In your home, you'll find 240V single-phase powering your clothes dryer, electric oven, and possibly your central air conditioner. These appliances require more power than standard 120V circuits can provide, but they don't need the continuous, high-capacity power of a three-phase system. Think of it as needing a boost of energy, but not a constant barrage.
Now, picture a large manufacturing facility. You'll likely see massive electric motors powering assembly lines, robotic arms, and ventilation systems. These motors need the consistent and powerful torque that only three-phase power can deliver. Without it, the machinery would run inefficiently or simply fail to operate. It's akin to needing a steady supply of fuel to keep a long journey on track.
Beyond factories, you'll also find three-phase power in hospitals, data centers, and other critical infrastructure where uninterrupted power is essential. The redundancy and stability of three-phase systems ensure that sensitive equipment continues to operate even if one phase experiences a problem. Imagine a hospital relying on backup generators to ensure life-saving equipment functions without any disruption. The reliable and efficient nature of 3 phase is very critical here
So, when you see a 240V connection, don't jump to conclusions about it being three-phase. Check the wiring, consider the application, and think about the power requirements. It's all about context! A simple electrical outlet in your laundry room is vastly different from the main power feed into a factory. One's sipping tea, the other's running a marathon!

How Does 480v 3 Phase Work » Wiring
How to Identify the Phase
4. Tips for Distinguishing Between Single and Three-Phase
Alright, so how can you tell the difference between a 240V single-phase and a 240V three-phase connection in the real world? Here are a few clues to help you become an electrical detective. First, check the breaker panel. A single-phase 240V circuit will typically use a double-pole breaker, meaning it takes up two slots in the panel. A three-phase circuit will usually use a three-pole breaker, occupying three slots. Think of the breaker as the guardian of the circuit, and its size reveals the system's complexity.
Next, examine the wiring itself. A single-phase 240V circuit will typically have three wires: two hot wires and a neutral wire (plus a ground wire for safety). A three-phase circuit will have three hot wires, and potentially a neutral wire (again, plus a ground). The presence of that third hot wire is a telltale sign. It's like spotting an extra ingredient in a recipe — it changes the whole flavor!
Another clue can be found in the type of equipment being powered. As we've discussed, large motors and heavy machinery are almost always powered by three-phase electricity. If you see a massive motor humming away, chances are it's connected to a three-phase system. Imagine looking at a powerful race car. The components under the hood gives away the intention to move very fast.
Finally, if you're unsure, consult a qualified electrician. They can use a multimeter to measure the voltage between the wires and determine the phase configuration. Working with electricity can be dangerous, so it's always best to leave it to the professionals if you're not comfortable. After all, safety first! Always remember, "Measure twice, cut once" applies to electrical work too! It's better to call a professional than to become an unintended conductor.
How To Convert 3Phase Single Phase 220V, 240v And 120v, 49 OFF
Debunking Myths and Answering Your Questions
5. Addressing Common Misconceptions About Voltage and Phase
Let's tackle some common myths surrounding 240V and three-phase power. One frequent misconception is that three-phase power is inherently more dangerous than single-phase. While it's true that three-phase systems can deliver more power, the voltage itself isn't necessarily more dangerous. The risk depends on the current and the safety precautions taken. Imagine a powerful river; it's not the water itself that's dangerous, but the force of the current and the potential for drowning if you're not careful.
Another myth is that all 240V appliances can be easily converted to run on three-phase power. This is not always the case. The appliance needs to be specifically designed for three-phase operation, and the wiring and control systems need to be compatible. Trying to force a single-phase appliance to run on three-phase power could damage the appliance or create a safety hazard. It's like trying to fit a square peg into a round hole — it's not going to work without some serious modifications.
And finally, some people believe that three-phase power is only for large industrial applications. While it's true that it's commonly used in industry, three-phase power can also be beneficial in some residential situations, particularly for homes with high power demands or specialized equipment. However, the cost of installing and maintaining a three-phase system in a home is usually prohibitive unless there's a very specific need. Think of it like having a private jet — it's great if you need it, but most people can get by just fine with a regular car.
Understanding the nuances of voltage and phase is crucial for anyone working with electricity, whether you're a homeowner, an electrician, or an engineer. By debunking myths and clarifying common misconceptions, we can ensure safer and more efficient use of electrical power. Remember, knowledge is power (pun intended!).
240v 3 Phase 4 Wire
FAQ
6. Frequently Asked Questions About 240V and 3-Phase Systems
Q: Can I convert my home from single-phase to three-phase power?
A: It's technically possible, but it's a significant undertaking that usually requires upgrading your electrical panel, service entrance, and possibly even the transformer serving your home. The cost can be substantial, so it's generally only worth considering if you have a specific need for three-phase power, such as running heavy-duty machinery in a home workshop. It's usually not economical for typical residential use. Think of it like remodeling your entire kitchen just to make a single cup of coffee every morning - overkill!
Q: What are the advantages of three-phase power over single-phase?
A: Three-phase power offers several advantages, including more efficient power delivery, smoother motor operation, and the ability to handle higher loads. It's also more reliable, as a three-phase system can continue to operate even if one phase fails. These advantages make it ideal for industrial and commercial applications where high power demands and reliability are critical. It's kind of like having a backup plan for your backup plan!
Q: How do I know if my appliance requires 240V?
A: Check the appliance's nameplate, which should list the voltage and amperage requirements. You can also consult the owner's manual or the manufacturer's website. Common 240V appliances include electric stoves, dryers, water heaters, and some air conditioning units. If you're unsure, consult a qualified electrician. It's always better to be safe than sorry, especially when dealing with electricity!
Q: What happens if I plug a 120V appliance into a 240V outlet?
A: Uh oh! That's generally a recipe for disaster. Plugging a 120V appliance into a 240V outlet will likely cause it to overheat and potentially catch fire. It's like giving a small child a double dose of medicine - it's not going to end well. Always double-check the voltage requirements before plugging in any appliance.
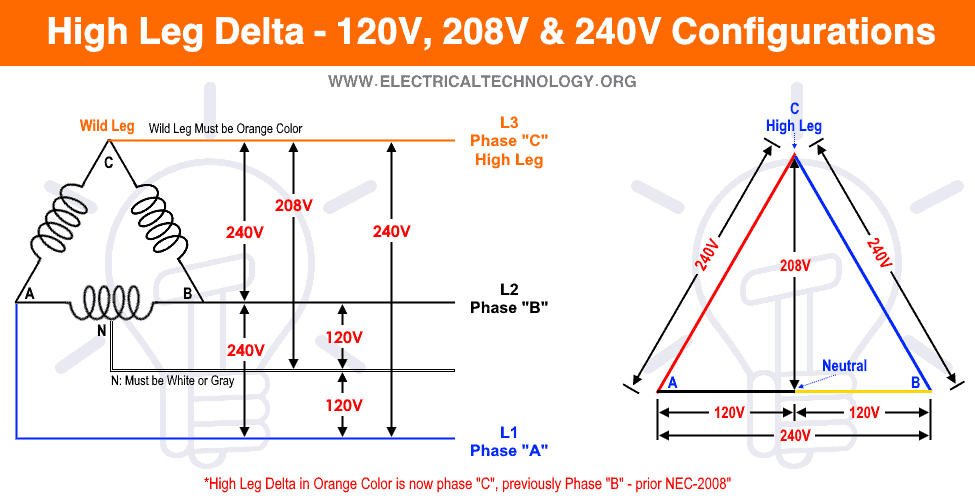
Q: Is 208V the same as 240V 3-phase?
A: Not quite. 208V is another common voltage level in three-phase systems, often used in commercial buildings. While both are three-phase, they're not interchangeable without proper consideration. Using equipment rated for one voltage on a system with the other voltage can lead to inefficiencies or even damage. It's like trying to use the wrong fuel in your car - it might run for a bit, but eventually, things will break down.